Trans-jugular Intrahepatic Porto-systemic Shunt
- Home
- Trans-jugular Intrahepatic Porto-systemic Shunt
Trans-jugular Intrahepatic Porto-systemic Shunt (TIPSS) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to manage complications of portal hypertension, particularly in individuals with chronic liver disease. This procedure creates a channel within the liver to connect the portal vein to a hepatic vein, reducing pressure and improving blood flow. TIPSS is a life-saving intervention for conditions such as refractory gastrointestinal bleeding and recurrent ascites.
Portal hypertension, a common consequence of liver dysfunction, can lead to severe complications if untreated. TIPSS provides a vital alternative for patients who have not responded adequately to medical therapy, significantly enhancing their prognosis and quality of life. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, benefits of early treatment, the latest TIPSS techniques, and provide answers to common questions to help you better understand this advanced procedure.
Glossary of Terms
- Portal Hypertension: Increased blood pressure within the portal vein system, often caused by liver scarring.
- Varices: Enlarged veins in the esophagus or stomach that can rupture and bleed.
- Ascites: Fluid buildup in the abdomen due to liver dysfunction.
Causes
TIPSS is primarily indicated for patients with complications arising from portal hypertension. This condition is often caused by:
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver due to chronic liver disease, alcohol abuse, or hepatitis.
- Hepatic Vein Obstruction: Conditions such as Budd-Chiari syndrome that block venous outflow from the liver.
- Portal Vein Thrombosis: Blood clots in the portal vein that hinder proper blood flow.
- Chronic Hepatitis: Long-term liver inflammation can contribute to portal hypertension, exacerbating symptoms over time.
These underlying causes lead to increased portal vein pressure, resulting in complications such as variceal bleeding and ascites. Identifying the root cause is essential for tailoring effective treatment strategies.
Symptoms
Patients who may benefit from TIPSS often present with:
- Severe gastrointestinal bleeding: Vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stools due to esophageal or gastric varices.
- Abdominal swelling: Caused by fluid accumulation (ascites).
- Encephalopathy: Confusion or altered mental states due to toxins not being processed effectively by the liver.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicating liver dysfunction.
- Fatigue: A common symptom resulting from liver dysfunction and fluid retention.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent severe complications. Regular monitoring of liver function tests and imaging studies can help detect portal hypertension before symptoms worsen.
Benefits of Early Treatment
Undergoing TIPSS early offers numerous advantages:
- Control of Bleeding: Prevents life-threatening hemorrhages from ruptured varices.
- Symptom Relief: Reduces ascites, improving comfort and quality of life.
- Improved Liver Function: Eases pressure on the liver, potentially slowing disease progression.
- Minimized Hospitalizations: Reduces the frequency and severity of complications, leading to fewer emergency visits.
- Enhanced Nutritional Status: Relieving ascites can improve appetite and nutrient absorption.
- Prevention of Complications: Early intervention can prevent the escalation of portal hypertension complications, such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP).
Latest Treatment Techniques
TIPSS has evolved significantly with advancements in medical imaging and interventional radiology. Modern techniques ensure higher success rates and fewer complications. Key aspects include:
- Imaging Guidance: Real-time ultrasound and fluoroscopy aid precise placement of the shunt.
- Stent Technology: Covered stents (e.g., polytetrafluoroethylene or PTFE-covered stents) improve patency rates, reducing the risk of blockage.
- Adjunctive Therapies: Combining TIPSSS with medications or additional procedures (e.g., variceal banding) for comprehensive care.
- Personalized Treatment Planning: Tailoring the procedure to the patient’s anatomy and clinical condition ensures optimal outcomes.
- Post-Procedure Monitoring: Advances in imaging and biomarkers help in tracking shunt performance and identifying potential complications early.
These advancements have made TIPSS safer and more effective, with improved long-term outcomes for patients with severe liver disease.
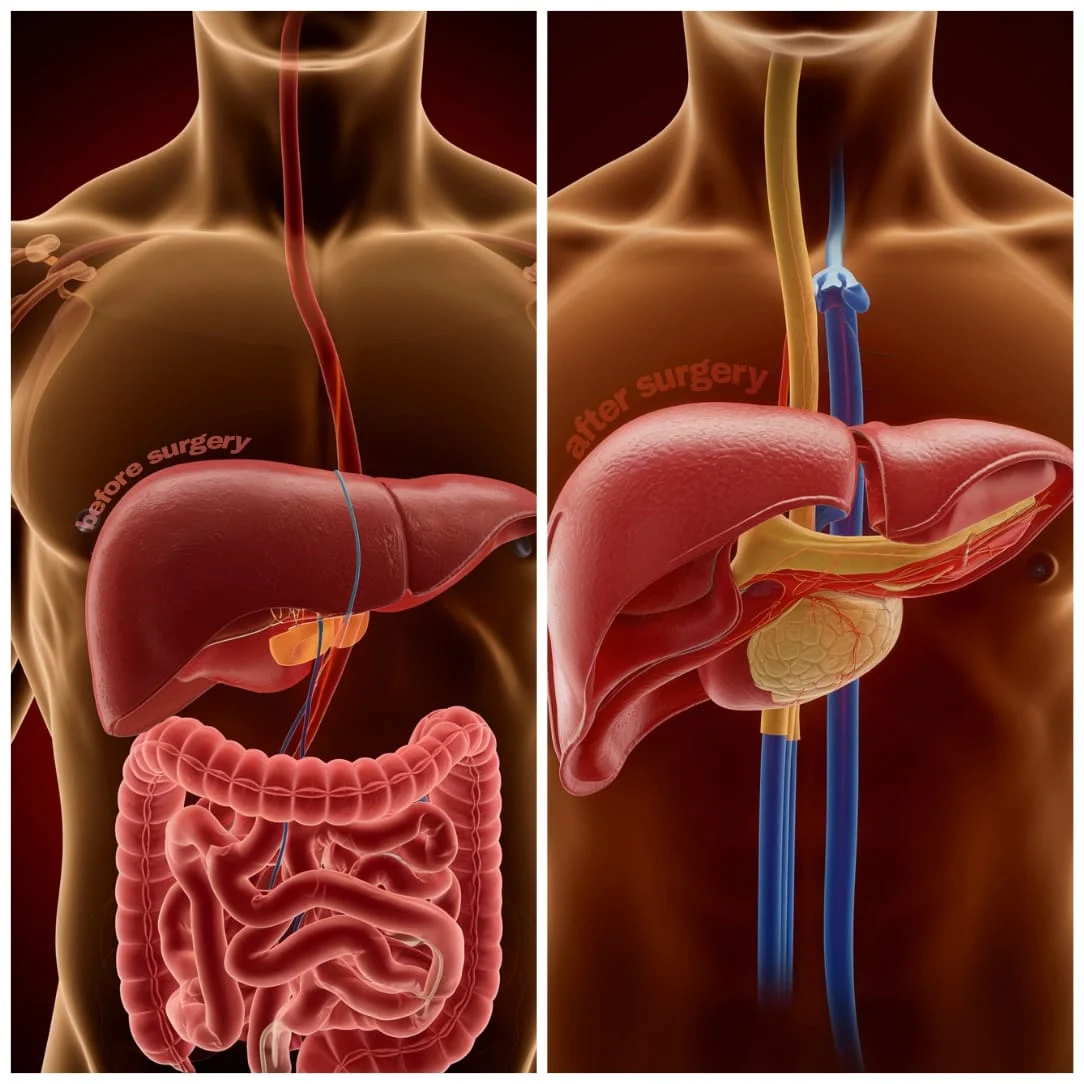
Conclusion
Trans-jugular Intrahepatic Porto-systemic Shunt (TIPSS) is a revolutionary procedure for managing complications of portal hypertension. Its minimally invasive nature and high success rate make it a cornerstone of modern hepatology care.
TIPSS is not only a treatment but also a gateway to improved quality of life for individuals battling the complications of liver disease. Early recognition of symptoms, combined with timely medical intervention, can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the burden of severe complications.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding or related liver conditions, consult a specialist immediately to explore your treatment options. Early intervention can save lives and significantly improve quality of life.
For expert advice or to book a consultation, contact us here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
TIPSS is a minimally invasive procedure that creates a bypass between the portal and hepatic veins to reduce portal hypertension. This helps prevent complications like variceal bleeding and ascites.
Patients with refractory variceal bleeding, recurrent ascites, or severe portal hypertension despite medical management are ideal candidates. It is also suitable for individuals at high risk of complications from portal hypertension.
While TIPSS significantly improves symptoms, it does not cure the underlying liver disease. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor shunt function and liver health.
Like any medical procedure, TIPSS carries risks, including encephalopathy, infection, or stent blockage. However, these risks are minimized with proper management and regular monitoring.
Recovery varies but is typically quick. Most patients resume normal activities within a week, but ongoing monitoring is required to ensure the shunt remains functional and effective.
For some patients, alternative treatments like variceal banding, sclerotherapy, or paracentesis may be considered, depending on the severity of their condition and overall health.
Patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy diet, limit alcohol intake, and attend regular medical check-ups to ensure optimal outcomes.
Many insurance providers cover TIPSS, but it’s essential to check with your provider about specific terms and coverage details.
For more insights into liver interventions, check out our page on Liver Intervention or learn about advanced vascular surgery costs.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms, contact us today to schedule a consultation. Our experienced specialists will help you choose the best treatment for your condition.
