Cerebral Angiography
- Home
- Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography is a diagnostic procedure that visualizes blood vessels in the brain. It is essential for diagnosing conditions like aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), stenosis, and blockages. This procedure helps doctors detect vascular issues in the brain, leading to more effective treatment planning and improved patient outcomes.
Cerebral angiography is often recommended for patients with symptoms such as severe headaches, dizziness, or neurological deficits that suggest brain vascular problems.
Causes of Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography is typically used to investigate the following conditions:
- Aneurysms: Abnormal bulges in blood vessels that can rupture, causing life-threatening bleeding.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Abnormal connections between arteries and veins that can lead to strokes or brain hemorrhages.
- Stenosis: Narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup or vascular diseases, increasing stroke risk.
- Brain Tumors: Assessing the blood supply to tumors for treatment planning.
- Stroke: Identifying the cause of a stroke, such as blocked or narrowed arteries.
- Trauma: Brain injuries affecting blood vessels may also require angiography for evaluation.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Cerebral Angiography
Symptoms that may suggest the need for cerebral angiography include:
- Severe Headaches: Sudden, intense headaches often linked to aneurysms or AVMs.
- Vision Changes: Sudden vision loss, double vision, or blurriness due to vascular issues.
- Dizziness or Vertigo: A feeling of imbalance caused by impaired blood flow.
- Numbness or Weakness: Particularly on one side of the body, a sign of a stroke or vascular malformation.
- Speech Difficulty: Problems with speech or understanding language, indicating a stroke or brain aneurysm.
- Seizures: Unexplained seizures, potentially caused by AVMs or other brain conditions.
If these symptoms occur, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation and determine the need for cerebral angiography.
Benefits of Early Treatment for Cerebral Angiography
Early diagnosis through cerebral angiography offers several advantages:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Provides detailed images of brain blood vessels to identify aneurysms, AVMs, and blockages.
- Timely Treatment: Early detection reduces the risk of complications like aneurysm rupture or stroke.
- Improved Outcomes: Early intervention increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
- Better Treatment Planning: Helps doctors devise the most effective treatment strategies.
Latest Treatment Techniques for Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography plays a key role in diagnosing and treating brain vascular conditions. Here are some techniques:
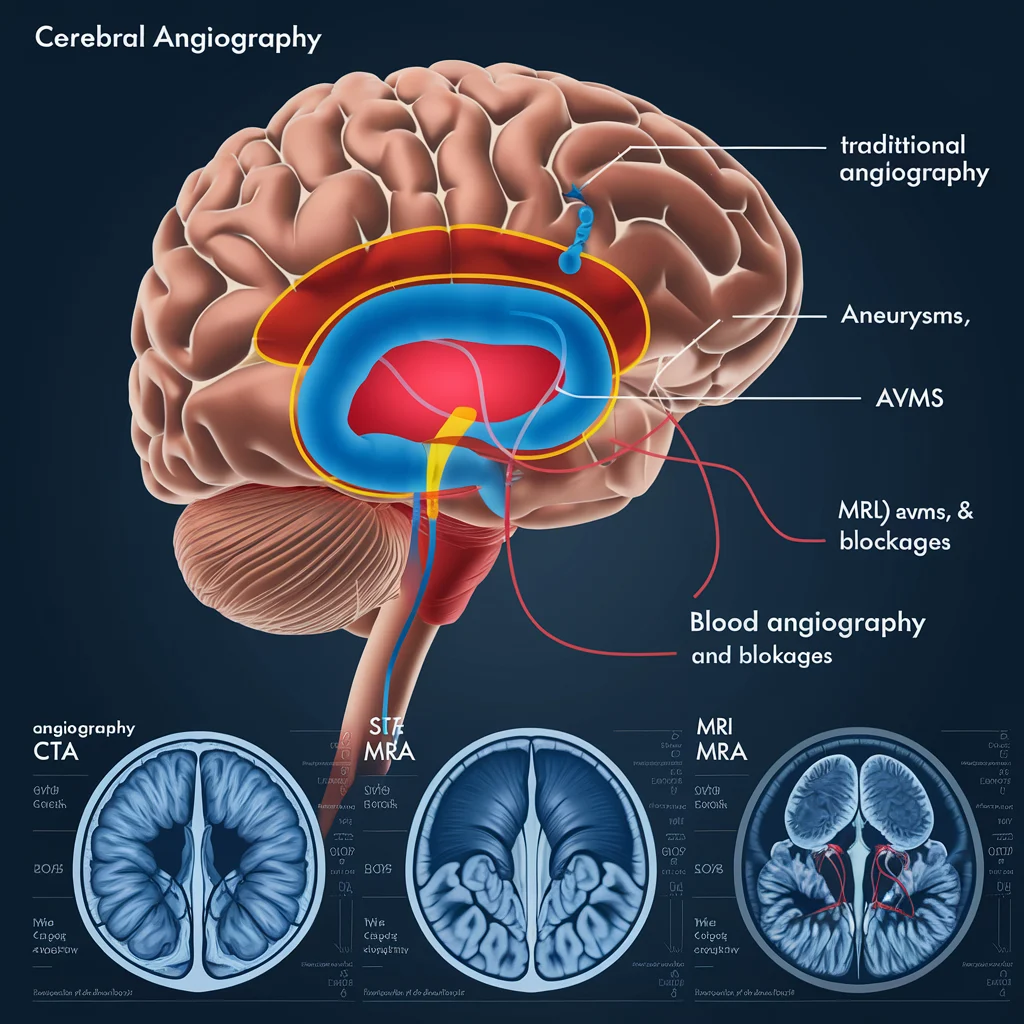
1. Traditional Cerebral Angiography
Injects contrast dye into the arteries and captures X-ray images of the brain’s blood vessels. It is highly effective for detecting aneurysms, AVMs, and blockages.
Example: A patient with a brain aneurysm may undergo this procedure to assess its size and location.
Pros:
- High-resolution images
- Effective for detecting vascular abnormalities
2. CT Angiography (CTA)
Uses a CT scanner with contrast dye to visualize blood vessels. It is faster than traditional angiography and often used initially.
Example: A patient with stroke symptoms may undergo CTA to quickly identify blockages or hemorrhages.
Pros:
- Quick and non-invasive
- Provides detailed images of blood vessels
3. MR Angiography (MRA)
MRA uses MRI with contrast dye to visualize blood vessels. It is particularly useful for detecting AVMs and other vascular conditions.
Example: MRA may be used to identify AVMs in a patient with unexplained seizures.
Pros:
- Non-invasive, no radiation
- Provides high-resolution images
4. Endovascular Coiling for Aneurysms
Endovascular coiling is used to treat aneurysms identified through cerebral angiography. Small coils are placed inside the aneurysm to prevent rupture.
Example: A patient with an aneurysm detected through angiography may undergo coiling to secure it.
Pros:
- Minimally invasive
- Reduces rupture risk
5. Stenting for Arterial Blockages
When arteries are narrowed, a stent can be placed to reopen the artery during cerebral angiography.
Example: A patient with carotid artery stenosis may undergo stenting to restore blood flow.
Pros:
- Minimally invasive
- Restores blood flow

Conclusion
Cerebral angiography is a vital tool in diagnosing and treating brain vascular conditions. Early diagnosis leads to better treatment outcomes, preventing complications like strokes or aneurysms. Whether through traditional angiography, CTA, or MRA, this procedure helps doctors plan effective treatments, improving patient recovery and quality of life.
If you suspect a vascular issue in the brain, contact a healthcare provider to explore diagnostic and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It visualizes the blood vessels in the brain to diagnose conditions like aneurysms, AVMs, and blockages.
The procedure is generally safe, though risks include bleeding or allergic reactions to the contrast dye.
Recovery is typically quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a day, especially with non-invasive techniques like CTA or MRA.
Risks include infection, bleeding, or complications from the contrast dye, though these are rare and manageable.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms of brain vascular issues, contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore your treatment options. Early diagnosis can prevent serious complications and improve your health outcomes.
