Biliary Drainages
- Home
- Biliary Drainages
Drainage is a medical procedure used to remove excess fluids, pus, or other substances from the body. It is commonly performed to treat infections, abscesses, or fluid buildup in areas such as the chest, abdomen, or joints. Drainage helps alleviate discomfort, promote healing, and prevent complications. This guide provides a detailed overview of drainage treatment, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Causes for Drainage Treatment
Drainage is typically required when there is an accumulation of fluid or pus in the body, often due to:
- Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can lead to abscesses that require drainage to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Trauma: Physical injury can cause fluid buildup in the tissues, requiring drainage to remove blood or other fluids.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: After surgery, fluid buildup around the surgical site may require drainage to prevent infection or swelling.
- Chronic Conditions: Diseases such as liver cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, or kidney disease can lead to fluid accumulation in the abdomen or lungs (ascites or pleural effusion), requiring drainage.

Symptoms Indicating the Need for Drainage
Signs that may indicate the need for drainage include:
- Pain or Swelling: Persistent swelling or pain near an infection or injury site may suggest fluid buildup.
- Fever: A fever, especially with swelling, may indicate an infection requiring drainage.
- Discharge: Pus or foul-smelling discharge from a wound or surgical site may signal an abscess or infection that requires drainage.
- Breathing Difficulty: Fluid accumulation in the lungs (pleural effusion) can cause difficulty breathing, necessitating drainage.
If you experience these symptoms, seeking medical advice is crucial to determine if drainage is necessary.
Treatment Options for Drainage
Several treatment options are available depending on the location and cause of fluid buildup. These include:
1. Percutaneous Drainage
Description: A minimally invasive procedure where a small catheter is inserted through the skin to drain fluid. It is guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT scans.
Example: Commonly used for abscesses in the liver or kidneys, where a catheter removes pus or infected fluid.
2. Endoscopic Drainage
Description: Uses an endoscope (a flexible tube with a camera) to locate and drain fluid from the chest or abdomen. This technique requires minimal incisions.
Example: Used to treat bile duct obstructions or pancreatic pseudocysts. In cases of a pancreatic pseudocyst, fluid around the pancreas is drained using this method.

3. Closed Drainage Systems
Description: A sealed drainage tube connected to a collection bag, which continuously removes fluid from the body. This system reduces the risk of infection.
Example: Often used after surgeries like mastectomies or hip replacements to remove excess fluid from the surgical site.
4. Surgical Drainage
Description: In severe cases, a larger incision may be made to remove large fluid accumulations or abscesses that cannot be drained percutaneously.
Example: Used for large perianal abscesses, where surgery is necessary to create a passage for pus drainage.
5. Chest Tube Drainage
Description: A tube is inserted into the chest cavity to drain fluid or air, typically used in cases of pleural effusion or post-trauma to the chest.
Example: In patients with pleural effusion caused by congestive heart failure, a chest tube is inserted to drain excess fluid, allowing for easier breathing.
6. Abdominal Drainage
Description: A tube or catheter is inserted into the abdomen to remove fluid buildup, often due to conditions like ascites or infections.
Example: In patients with liver cirrhosis, abdominal drainage can relieve symptoms of fluid retention and prevent complications like infection.
Benefits of Early Drainage Treatment
Early drainage has several advantages:
- Prevention of Infection: Drainage helps remove infected material, reducing the risk of infection spreading.
- Relief from Pressure: Removing fluid helps alleviate the pressure caused by fluid buildup, reducing discomfort.
- Faster Recovery: Timely drainage prevents further fluid accumulation and promotes quicker healing.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Conditions: Early intervention can prevent the development of chronic issues like pleural effusion or ascites.
Conclusion
Drainage is an essential procedure for managing fluid buildup, infections, and other medical conditions. Whether performed minimally invasively or through surgery, drainage helps reduce pain, prevent infection, and speed up recovery. If you’re experiencing symptoms like swelling, pain, or difficulty breathing, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if drainage is necessary for your condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Percutaneous drainage involves the insertion of a catheter through the skin to drain fluids, often guided by ultrasound or CT scans.
Recovery time varies. Percutaneous drainage typically requires a short recovery, while surgical drainage may take longer.
Drainage procedures are generally minimally invasive, and local anesthesia is used. Mild discomfort may occur afterward.
Yes, drainage is commonly used to remove fluid from the lungs in cases of pleural effusion, improving breathing and comfort.
Though generally safe, risks include infection, bleeding, or injury to surrounding tissues. However, these risks are minimal when the procedure is performed by a skilled healthcare provider.
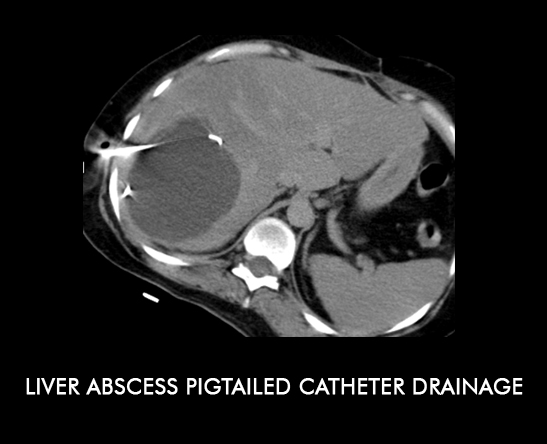
CASE 1
45yr male with pain in the abdomen and fever since 7days. On sonography, there was a large right lobe liver abscess. Pigtailed Catheter inserted for continuous drainage of the collection.
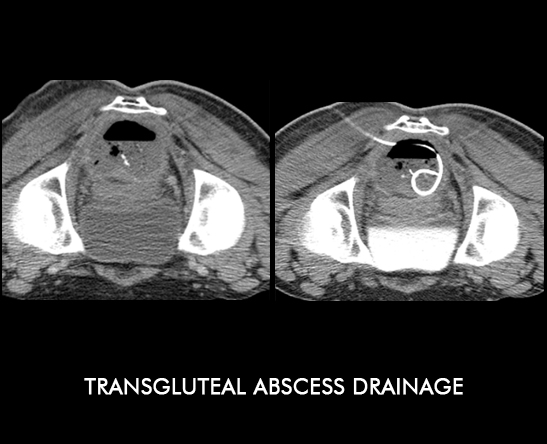
CASE 2
42yr male patient with a post operative large transgluteal collection with air pockets suggestive of infective pathology, needed drainage. A pigtailed catheter inserted.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms of brain vascular issues, contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore your treatment options. Early diagnosis can prevent serious complications and improve your health outcomes.
