Biopsy Test
- Home
- Biopsy Test
A biopsy test is a critical procedure that involves removing a small sample of tissue from the body for laboratory analysis. It helps in diagnosing various conditions, particularly cancer, and other diseases like infections or inflammatory conditions. Whether you are preparing for a biopsy due to specific symptoms or have been advised to undergo one for diagnostic purposes, this guide will walk you through the process, the different types of biopsies, and what you can expect before and after the procedure.
What is a Biopsy Test?
A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue is taken from the body to examine for any abnormalities. It is a key tool in diagnosing conditions such as cancer, infections, or inflammatory diseases. The biopsy sample is analyzed under a microscope by a pathologist who checks for signs of disease.
Biopsies are typically performed under local anesthesia, meaning the patient remains awake, but the area being tested is numbed to prevent discomfort. In some cases, general anesthesia may be required. Depending on the location of the tissue being sampled, biopsies are performed through a needle, endoscope, or during surgery.
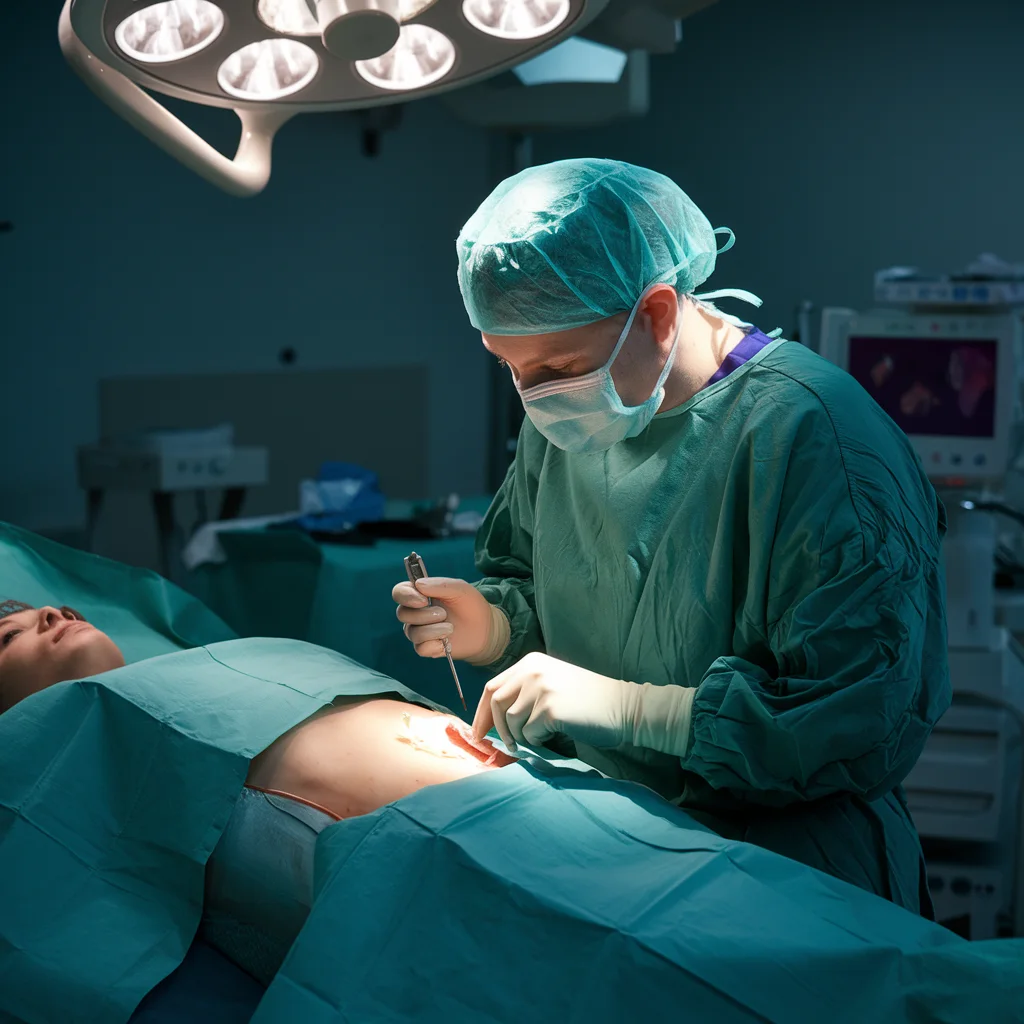
Types of Biopsy Tests
There are several different types of biopsy tests, each used depending on the location and nature of the condition. Some of the most common types include:
1. Needle Biopsy
- Core Needle Biopsy: A larger needle is used to remove a tissue sample, often used for solid masses in organs like the liver or lungs.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): A thinner needle extracts a smaller sample, typically used for thyroid, lymph node, or breast biopsies.
2. Endoscopic Biopsy
- An endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera, is used to look inside organs such as the colon, lungs, or bladder to take tissue samples.
3. Surgical Biopsy
- In cases where the tissue cannot be accessed with a needle or endoscope, a surgical biopsy may be necessary. This is typically done under general anesthesia.
4. Skin Biopsy
- A small section of skin is removed to test for conditions like skin cancer or other dermatological issues.
5. Bone Marrow Biopsy
- This test examines the bone marrow, commonly used for diagnosing blood cancers like leukemia.
When is a Biopsy Test Recommended?
A doctor may recommend a biopsy when a patient has symptoms that suggest an abnormality, such as:
- Unexplained lumps or masses
- Persistent pain or swelling
- Abnormal skin lesions or changes in existing moles
- Abnormal blood test results that suggest cancer or other diseases

Benefits of Early Biopsy Testing
Biopsy testing can provide several benefits, especially when done early:
- Accurate Diagnosis: A biopsy is often the only definitive way to confirm a diagnosis, especially for conditions like cancer.
- Targeted Treatment: Knowing the exact type of disease enables doctors to create a targeted treatment plan.
- Early Detection: Early detection can lead to more effective treatment and better recovery outcomes.
Latest Techniques in Biopsy Testing
Recent advancements have improved biopsy testing, making it more accurate and less invasive. Some new techniques include:
1. Liquid Biopsy
A promising new method for detecting cancer markers from a simple blood sample. It’s less invasive and offers early detection, especially for lung and breast cancer.
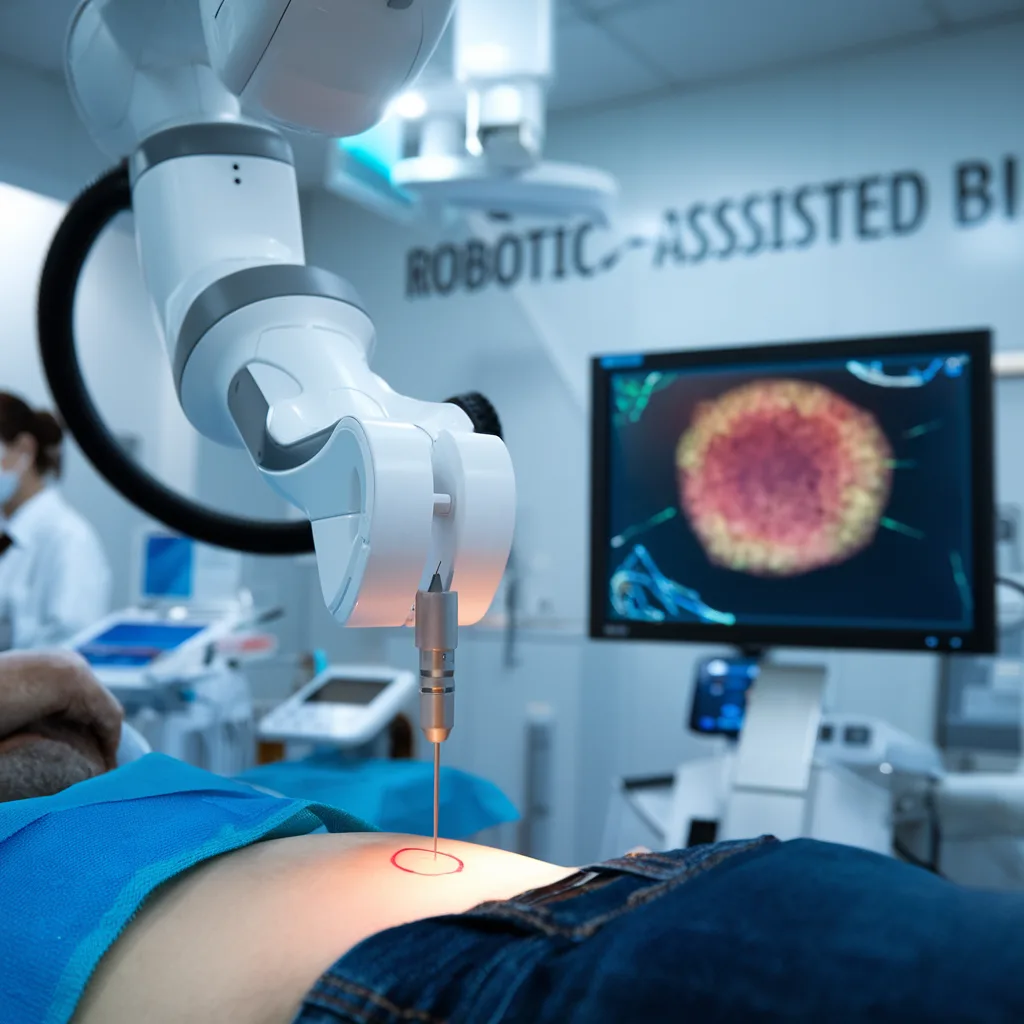
2. Robotic-Assisted Biopsy
Robotic systems offer enhanced precision when accessing difficult-to-reach areas.
3. Virtual Biopsy
Virtual biopsies use imaging technology such as MRI or CT scans to detect abnormalities without the need for physical tissue removal.
Conclusion
Biopsy tests are crucial for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, including cancers and infections. They allow doctors to identify the underlying causes of symptoms, enabling more effective and targeted treatment plans. If your doctor has recommended a biopsy, rest assured that it is a reliable way to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Biopsies can diagnose cancer, infections, inflammatory diseases, and benign growths.
Biopsy results typically take a few days to a week. Your doctor will explain the expected timeline based on the test type.
While generally safe, risks include infection, bleeding, or damage to surrounding tissues. Your healthcare provider will discuss the specific risks before the procedure.
If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a doctor to evaluate whether a biopsy is necessary.
Biopsies do not prevent cancer, but they are essential for early detection, which can improve treatment outcomes.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms of brain vascular issues, contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore your treatment options. Early diagnosis can prevent serious complications and improve your health outcomes.
