Arterial Thrombosis
- Home
- Arterial Thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery, obstructing blood flow to vital organs like the heart, brain, or legs. This blockage can lead to severe complications, including heart attacks, strokes, or limb loss. Early detection and treatment are crucial to minimize damage and improve recovery.
This article explores the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the benefits of early intervention for arterial thrombosis.
Causes of Arterial Thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis is caused by conditions that promote blood clot formation in arteries. Key causes include:
- Atherosclerosis: Fatty deposits in arteries leading to clot formation, often causing heart attacks or strokes.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: High blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol damage arteries, promoting clotting.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like thrombophilia make blood more likely to clot.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and accelerates clotting.
- Arterial Injury: Trauma or surgery may trigger clot formation in the affected artery.
These conditions significantly impact daily life and require timely, effective treatment.
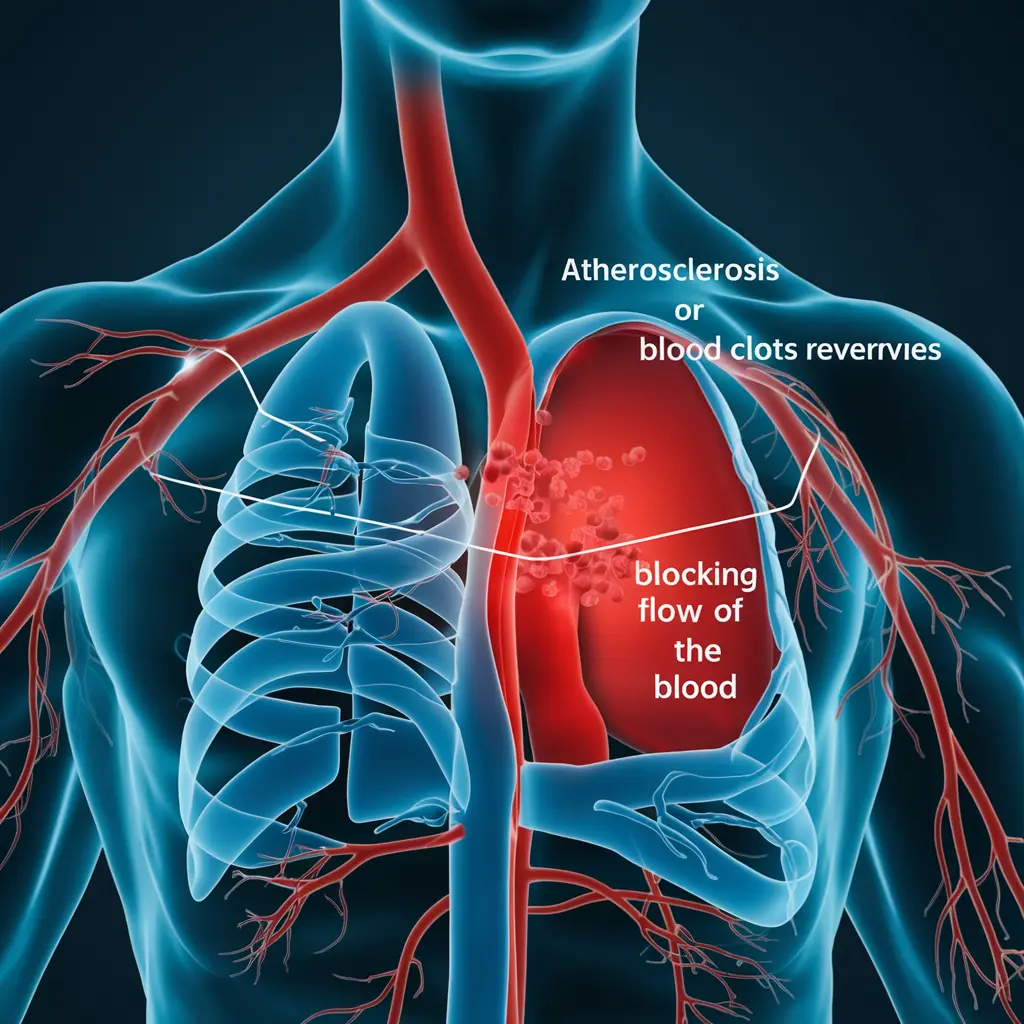
Symptoms of Arterial Thrombosis
Symptoms of arterial thrombosis depend on which artery is affected. Common signs include:
- Chest Pain: Often associated with a heart attack.
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: A sign of a stroke caused by a clot in brain arteries.
- Breathing Difficulty: Caused by a clot in the lungs.
- Leg or Arm Pain: A clot in the limb arteries can cause pain, coldness, or swelling.
- Vision Changes: A clot affecting eye arteries may cause sudden vision loss or blurred vision.
Seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.

Benefits of Early Treatment for Arterial Thrombosis
Prompt treatment offers several benefits:
- Prevention of Stroke or Heart Attack: Early intervention restores blood flow, preventing fatal complications.
- Minimized Tissue Damage: Quick treatment can reduce organ or limb damage, lowering the risk of amputations.
- Lower Recurrence Risk: Treating the condition reduces the chances of future clots.
- Improved Recovery: Faster recovery from symptoms like pain, swelling, and shortness of breath.
Latest Treatment Techniques for Arterial Thrombosis
Several treatment options are available depending on the severity and location of the clot:
1. Anticoagulation Therapy
Anticoagulants, or blood thinners, prevent new clots from forming and help dissolve existing ones. Common medications include warfarin, heparin, and newer oral anticoagulants.
Example: A patient with a clot in the leg artery may initially receive heparin and then switch to warfarin for long-term management.
Pros:
- Reduces clotting risk
- Essential for prevention and treatment
- Can be combined with other therapies
2. Thrombolytic Therapy
Thrombolytics are clot-busting drugs used to dissolve clots, often in emergencies like heart attacks or strokes. This treatment restores blood flow quickly.
Example: A heart attack patient may receive thrombolytics to dissolve the clot blocking the coronary artery.
Pros:
- Rapid clot dissolution
- Restores blood flow in acute situations
- Life-saving in emergencies
3. Angioplasty and Stenting
Angioplasty uses a balloon to open blocked arteries, and stents are placed to keep them open. These methods are commonly used for coronary and carotid artery blockages.
Example: A patient with carotid artery blockage may undergo angioplasty and stenting to restore blood flow to the brain.
Pros:
- Minimally invasive with quick recovery
- Prevents re-narrowing of arteries
- Effective for restoring blood flow
4. Surgical Thrombectomy
In cases where other treatments are ineffective, a thrombectomy is performed to remove the clot surgically. It’s typically done for severe cases of limb ischemia.
Example: A patient with a blocked artery in the leg may undergo a thrombectomy to remove the clot and restore circulation.
Pros:
- Immediate clot removal
- Essential for critical cases
- Restores blood flow in blocked arteries

Conclusion
Arterial thrombosis is a serious condition that requires prompt intervention to prevent life-threatening complications like stroke, heart attack, or limb loss. Early diagnosis and treatment—whether through anticoagulation therapy, thrombolytics, angioplasty, or thrombectomy—can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term damage.
If you suspect you have arterial thrombosis, seek immediate medical attention to ensure the best possible treatment and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It’s caused by atherosclerosis, blood disorders, high cholesterol, and other risk factors that damage the arteries.
Symptoms include chest pain, difficulty breathing, weakness, leg pain, and vision changes.
Treatment typically includes anticoagulants, thrombolytics, angioplasty, or surgery, depending on the severity and location of the clot.
Preventative measures include managing cholesterol, blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms related to any of these conditions, contact us today for a consultation. Our specialists will help you find the best treatment options for your health and well-being.
