Acute Stroke Management
- Home
- Acute Stroke Management
Acute stroke management refers to immediate care provided to patients experiencing a stroke, a sudden disruption in blood supply to the brain. Stroke is a leading cause of death and long-term disability, making timely intervention crucial. Early diagnosis and effective management can reduce brain damage, prevent complications, and improve recovery chances.
This article discusses the causes of stroke, symptoms, the importance of early treatment, and the latest techniques used in stroke management.
Causes of Stroke
There are two primary types of strokes:
- Ischemic Stroke: Occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain, often due to atherosclerosis or embolism.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, leading to bleeding. It is commonly caused by high blood pressure, aneurysms, or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
Other causes include Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs), also known as mini-strokes, where symptoms are temporary but serve as a warning for future strokes.
Symptoms of Stroke
Recognizing stroke symptoms quickly is critical for effective treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden Numbness or Weakness: Often on one side of the body, affecting the face, arm, or leg.
- Sudden Confusion or Difficulty Speaking: Difficulty understanding speech or speaking clearly.
- Sudden Vision Problems: Blurred or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Sudden Severe Headache: Especially in hemorrhagic strokes.
- Loss of Coordination or Balance: Difficulty walking, dizziness, or lack of coordination.
If these symptoms are observed, seek emergency medical care immediately. Prompt treatment can help prevent permanent damage and improve recovery chances.

Benefits of Early Treatment
Early treatment is essential for minimizing brain damage and improving the chances of a full recovery. Benefits include:
- Prevention of Brain Damage: Early interventions restore blood flow or control bleeding, limiting brain cell damage.
- Reduced Disability: Timely treatment reduces the likelihood of long-term disability, helping patients regain functionality.
- Improved Prognosis: The sooner a stroke is treated, the better the patient’s chance of a successful recovery.
- Better Treatment Planning: Identifying the stroke’s cause early allows for tailored treatment, which enhances outcomes.
Latest Treatment Techniques for Acute Stroke Management
The approach to treating acute strokes varies depending on the type and severity. The goal is to restore blood flow or stop bleeding to minimize brain damage. Here are some of the latest treatment techniques:
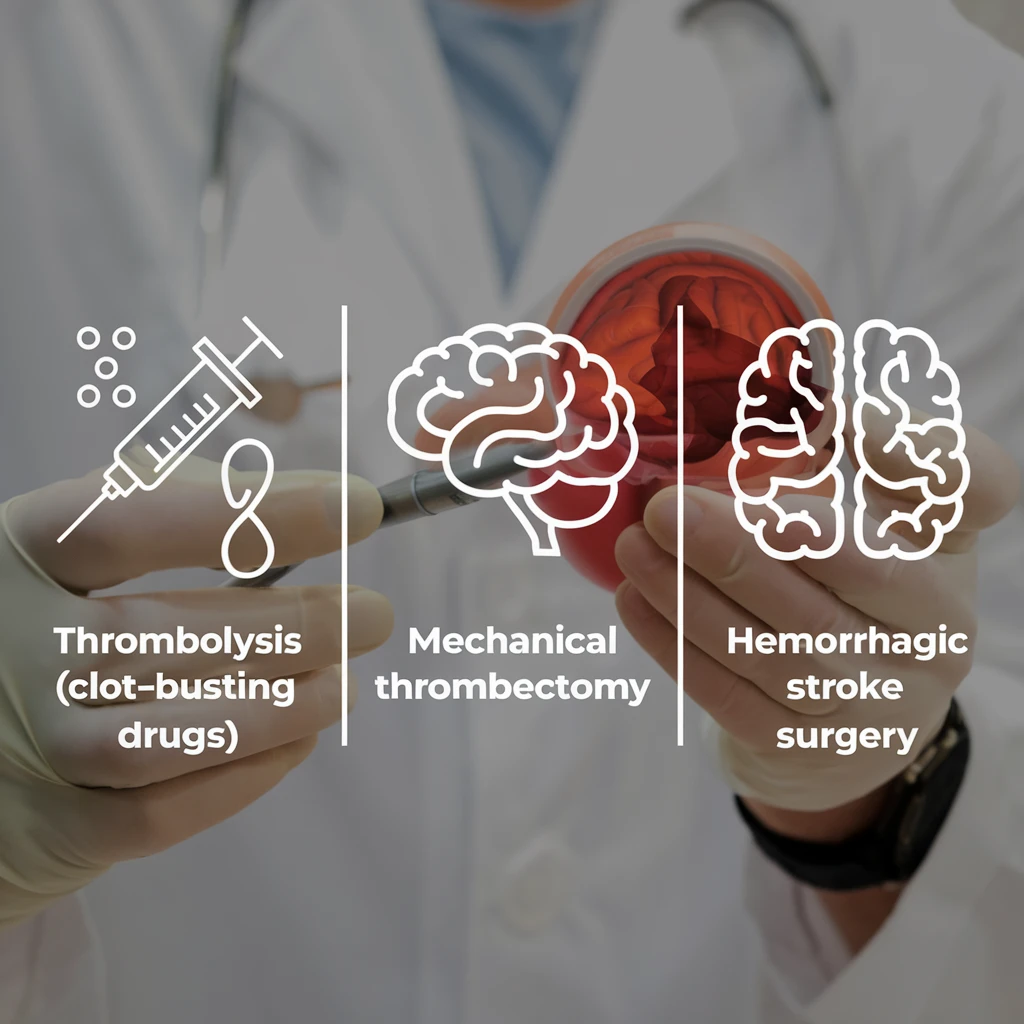
1. Thrombolysis (Clot-Busting Drugs)
For ischemic strokes, thrombolysis is the primary treatment. It involves the administration of tPA (tissue plasminogen activator) to dissolve blood clots and restore blood flow to the brain. This is most effective if administered within 3-4.5 hours of stroke onset.
Example: A patient with an ischemic stroke caused by a blood clot may receive tPA to break down the clot.
Pros:
- Minimizes brain damage when administered early.
- Highly effective for ischemic strokes if given within the first few hours.
2. Mechanical Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy is used when thrombolysis is not an option or when the clot is large. It involves inserting a catheter through the groin to physically remove the clot from the artery.
Example: A patient with a large clot blocking a major brain artery may undergo thrombectomy.
Pros:
- Highly effective for large vessel occlusions.
- Can be performed up to 24 hours after stroke onset.
3. Hemorrhagic Stroke Management
For hemorrhagic strokes, the focus is on controlling the bleeding and relieving pressure on the brain. Medications may be used to lower blood pressure, and surgical procedures like craniotomy may be performed to remove blood and repair damaged blood vessels.
Example: A patient with an aneurysm causing hemorrhagic stroke may require surgery to repair the blood vessel.
Pros:
- Stabilizes the patient.
- Prevents further bleeding or brain damage.
4. Neuroprotective Treatments
Neuroprotective therapies are still under investigation but hold promise in preventing brain cell death after a stroke. Though not yet widely used, these treatments aim to protect the brain and improve recovery after ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes.
Example: Experimental drugs that protect brain cells may be used in clinical trials for stroke patients.
Pros:
- Potential to improve recovery.
- Ongoing research to find effective treatments.
Conclusion
Acute stroke management is critical for preventing severe brain damage and improving patient outcomes. With rapid diagnosis and treatment options like thrombolysis, thrombectomy, and hemorrhagic stroke management, stroke patients have better chances of recovery. Early intervention is key to reducing long-term disability and enhancing recovery. If you experience stroke symptoms, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Strokes are caused by a blockage (ischemic stroke) or rupture (hemorrhagic stroke) of blood vessels in the brain, leading to lack of blood supply or bleeding.
Symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness, difficulty speaking, confusion, and severe headache. Immediate medical attention is necessary.
Clot-busting drugs like tPA and mechanical thrombectomy are commonly used for ischemic stroke treatment.
Recovery varies depending on the stroke’s severity. It typically involves rehabilitation therapies, including physical therapy and speech therapy, to regain lost functions.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms of brain vascular issues, contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore your treatment options. Early diagnosis can prevent serious complications and improve your health outcomes.
