Acute GI Bleed
- Home
- Acute GI Bleed
Acute gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a medical emergency that involves sudden bleeding from the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or colon. It can result in significant blood loss, shock, and even death if not treated promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical for preventing life-threatening complications. With the right treatment, most cases of acute GI bleeding can be controlled, and patients can recover effectively.
This article covers the causes, symptoms, and treatments of acute GI bleeding, highlighting the importance of early intervention and modern treatment techniques that improve patient outcomes.
Causes of Acute GI Bleed
Several conditions can lead to acute GI bleeding, including:
- Peptic Ulcers: Sores in the stomach or duodenum, often caused by Helicobacter pylori or NSAID use.
- Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining, usually caused by alcohol or medications like aspirin.
- Esophageal Varices: Enlarged veins in the esophagus, often caused by liver cirrhosis, that can rupture.
- Diverticular Disease: Small pouches in the colon that can bleed if ruptured.
- Colorectal Cancer: Tumors in the colon or rectum that may bleed.
- Angiodysplasia: Abnormal blood vessels in the GI tract that can cause bleeding.
- Mallory-Weiss Tear: A tear in the esophagus caused by severe vomiting.
- Trauma: Abdominal injuries affecting the GI trac

Symptoms of Acute GI Bleed
Symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the bleeding but typically include:
- Vomiting Blood (Hematemesis): Bright red or dark, coffee-ground vomit, indicating upper GI bleeding.
- Black, Tarry Stools (Melena): Black stools suggest bleeding in the upper GI tract.
- Bright Red Blood in Stool (Hematochezia): Fresh blood in stool typically indicates lower GI bleeding.
- Abdominal Pain: Pain often linked to ulcers, diverticulosis, or cancer.
- Dizziness or Weakness: Due to blood loss.
- Paleness and Cold, Clammy Skin: Signs of shock.
If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. The earlier the bleeding is addressed, the better the chance of a full recovery.

Benefits of Early Treatment for Acute GI Bleed
Early treatment provides several critical benefits:
- Prevention of Shock: Immediate intervention stabilizes blood pressure and prevents shock, a life-threatening condition caused by low blood volume.
- Reduced Mortality: Timely treatment significantly reduces the risk of death, especially in cases of severe bleeding like esophageal varices or large peptic ulcers.
- Improved Recovery: Addressing the bleeding source promptly helps patients recover more quickly and minimizes the need for extensive treatment.
- Better Treatment Planning: By identifying the bleeding cause early, doctors can plan the best course of action for effective management.
Latest Treatment Techniques for Acute GI Bleed
Several modern treatments are available for managing acute GI bleeding, depending on its severity and cause:
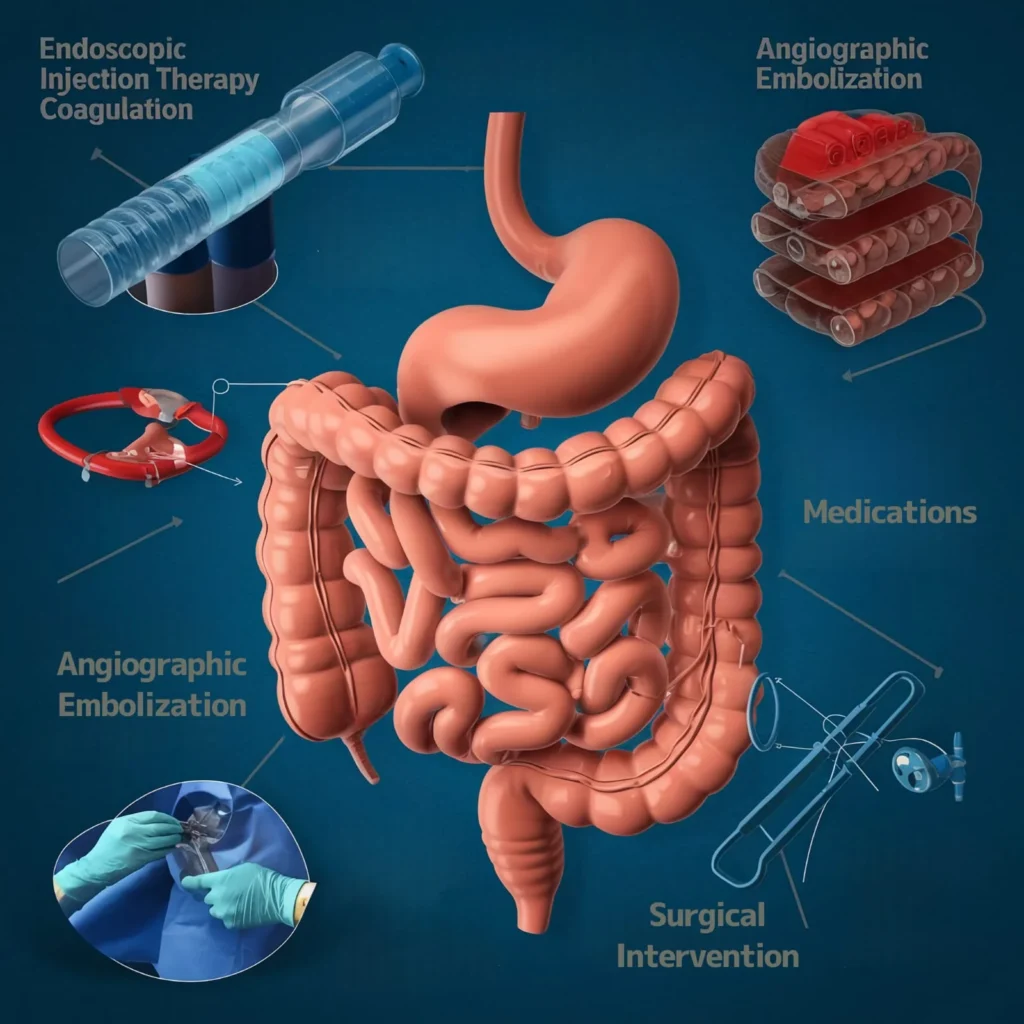
1. Endoscopic Therapy
Endoscopy is often the first treatment used to diagnose and control bleeding in the upper GI tract. The flexible tube inserted during endoscopy allows doctors to directly treat the source of bleeding using techniques like:
- Injection Therapy: Medications injected to constrict blood vessels and stop bleeding.
- Coagulation: Using heat or laser to coagulate and seal blood vessels.
- Hemostatic Clips: Placing clips to close bleeding blood vessels.
Example: A patient with an active peptic ulcer may undergo endoscopy to stop the bleeding.
Pros:
- Minimally invasive
- Quick and effective for most upper GI bleeds
2. Angiographic Embolization
If endoscopy fails or if bleeding is severe, angiographic embolization can be performed. A catheter is inserted into the blood vessels to inject small particles that block blood flow and control the bleeding.
Example: A patient with diverticular bleeding may require embolization if endoscopic methods are unsuccessful.
Pros:
- Minimally invasive
- Can be used for both upper and lower GI bleeds
3. Surgical Intervention
Surgery is used when bleeding cannot be controlled by endoscopy or angiography. This option is often necessary for conditions like colorectal cancer or massive bleeding from other sources.
Example: A patient with a colon tumor may need surgery to remove part of the colon and stop the bleeding.
Pros:
- Life-saving in severe cases
- Necessary when other treatments fail
4. Medications
Medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or octreotide are used to treat underlying causes like peptic ulcers or esophageal varices. PPIs reduce stomach acid, while octreotide helps constrict blood vessels, reducing bleeding risk.
Example: A patient with esophageal varices may receive octreotide to manage bleeding before undergoing endoscopic therapy.
Pros:
- Non-invasive
- Can be combined with other treatments for better outcomes
Conclusion
Acute GI bleeding is a serious condition that demands immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment through techniques like endoscopy, angiographic embolization, and surgery can prevent severe complications, save lives, and improve recovery. Early intervention is crucial for a better outcome, and seeking medical help immediately if you experience symptoms of GI bleeding is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Causes include peptic ulcers, esophageal varices, diverticulosis, colorectal cancer, and trauma.
Symptoms include vomiting blood, black or red stools, abdominal pain, dizziness, and weakness.
Treatments include endoscopy, angiographic embolization, medications, and surgery, depending on the cause.
Yes, if untreated, it can lead to shock, organ failure, or death. Early treatment is essential.
Would you like to request an appointment?
You can call on +91-98200 86520 for Appointments or fill the form below
If you’re experiencing symptoms of brain vascular issues, contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore your treatment options. Early diagnosis can prevent serious complications and improve your health outcomes.
